Robotic “Gradient Fridge” — Concept Blueprint
A vertically-shelved refrigerator/freezer that works like a robotic garage. It uses automated storage/retrieval, a controlled temperature gradient (coldest at the bottom, coolest at the top), and a pre-cool vestibule to accept warm foods before they enter cold storage.
1) High-Level Concept
- Form factor: Tall insulated cabinet (or bank of cabinets) with multiple shelf “bays” and a central lift/shuttle that moves totes/bins in/out.
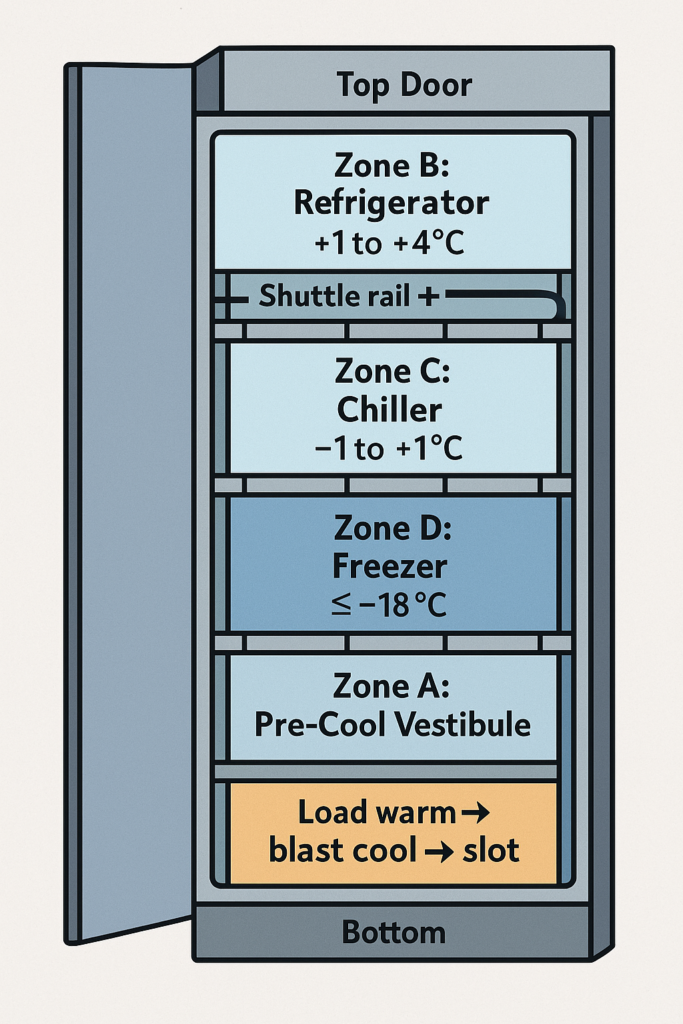
- Thermal profile:
- Zone A (Blast/Pre-Cool Vestibule): ~+25 to +45 °C (77–113 °F) down to ~10 °C (50 °F). Time-limited; heat is recovered.
- Zone B (Refrigerator): +1 to +4 °C (34–39 °F).
- Zone C (Chiller): −1 to +1 °C (30–34 °F) for meats/fish.
- Zone D (Freezer): −18 °C (0 °F) or colder.
- Automation: AS/RS mechanism (paternoster, shuttle, or elevator with telescoping fork) puts each tote where it belongs based on target temperature and FIFO.
- Interface: Touchscreen + QR/vision; app shows inventory, locations, and “ready” times.
2) Thermal & Airflow Design
- Natural stratification + active control: Coldest air wants to sink → place freezer at the bottom; use variable-speed fans and motorized dampers to keep zones sharp without mixing.
- Independent evaporator circuits: At least two loops:
- Loop 1: Freezer evap + sub-freezer buffer plate.
- Loop 2: Fridge/chiller evap with EEV for tight superheat control.
- Optional glycol loop to move cooling where needed without moving moist air.
- Zone partitions: Sliding baffle “gates” or insulated curtains around bays minimize exchange during shelf moves (like an air curtain in walk-ins).
- Moisture management:
- Dedicated defrost cycle for freezer coils (hot-gas or electric).
- Desiccant wheel or regenerative dehumidifier on vestibule to avoid frosting lower zones when doors open.
- Heat recovery: Waste heat from compressors and the pre-cool vestibule coil feeds a small domestic hot water or hand-wash loop.
3) Pre-Cool “Airlock” Workflow
- Load warm item into vestibule tote (lidded, drip-safe).
- Scan & classify (food type, mass, target zone, best-by).
- Thermal model estimates cool-down time using mass, specific heat, and heat-transfer coefficient.
- Blast-cool with high airflow over fin-tube coil until the core probe or IR surface confirms a safe entry temperature.
- Auto-transfer to its destination zone and start FIFO countdown.
Benefits: protects cold zones from heat spikes; captures and repurposes heat; improves food safety by quickly passing through the 54–21 °C (130–70 °F) and 21–5 °C (70–41 °F) danger ranges.
4) Storage Media (Totes/Bins)
- Uniform cylinders or rectangular totes with:
- Sealed lids + silicone gaskets to limit odor and moisture exchange.
- Embedded QR/NFC + optional UHF-RFID for hands-off ID.
- Food-safe liner inserts (dishwasher-safe).
- Color edges for human confirmation by zone (blue=fridge, gray=chiller, white=freezer).
- Weight cells in each bay to estimate remaining quantity; optional bin cameras for vision stock checks.
5) AS/RS Mechanics
- Options:
- Paternoster (continuous vertical loop of bins) for high access speed.
- Central elevator + shuttle fork to reach any bay (like warehouse shuttles).
- Spiral carousel for compact footprints.
- Requirements:
- Low-temp food-grade lubricants and sealed bearings.
- Condensation-resistant encoders and limit switches.
- Soft-close/soft-start motion profiles to avoid sloshing and pressure spikes.
- Safety: Light curtains, pinch-point guards, manual egress, UPS for parked position on power loss.
6) Controls & Software
- Sensing: NTC/PT100 probes per zone, door/baffle position, bay weight, vestibule IR + puncture probe, condenser/evap pressure transducers.
- Actuation: Variable-speed compressors (inverter), EEVs, EC fans, dampers, baffle gates, shuttle motors.
- Algorithms:
- Model-predictive control (MPC) balances zone temps, compressor power, and door events.
- Slotting optimizer: Stores items lower as they get colder; prioritizes FIFO and access frequency.
- Food safety rules: Alerts for core-temp not reached in time; rapid move to chiller if vestibule queue backs up.
- UI/Cloud:
- Pantry view, timers (“ready to portion in 18 min”), expiration radar, and meal-prep suggestions.
- API/webhooks for grocery integrations and recipe apps.
- Local edge control with offline mode; cloud only for analytics.
7) Food Safety & Standards (Design Targets)
- Refrigerator: ≤ 4 °C (≤ 39 °F).
- Chiller/raw proteins: −1 to +1 °C (30–34 °F) with tight tolerance.
- Freezer: ≤ −18 °C (≤ 0 °F).
- Cooling path: Hot foods through vestibule to ≤ 21 °C (70 °F) within 2 h, then to ≤ 4 °C (≤ 39 °F) within 4 h total (typical safe-cooling guidance).
- Materials: NSF/ANSI food-contact, smooth radiused corners, removable pans for sanitation, IP-rated electrics for washdown.
8) Energy Strategy
- Inverter compressors + floating head pressure for part-load efficiency.
- Night setback when doors won’t open (tighter baffles, lower fan speed).
- Door-open anticipation: Raise fan speed in active zones moments before moves; pre-chill target bay.
- Waste-heat reuse (hot water) and defrost scheduling during off-peak tariff windows.
- Optional DC bus + battery to ride through defrost peaks and short outages.
9) Manufacturing & BOM (MVP)
- Cabinet: Vacuum-insulated panels (VIP) + PU foam, heated mullions at interfaces.
- Refrigeration: 2 small variable-speed condensing units (R290 or R600a where permitted), plate/fin evaporators, EEVs.
- Mechanics: Aluminum extrusion frame for shuttle, food-safe belts/ball screws, stepper/BLDC with encoders.
- Electronics: STM32/ESP32 + CAN for zones, Raspberry Pi/CM for UI/vision, load cells, IR sensor, core probe.
- Totes: Injection-molded PP with TPE gasket; QR/NFC in-mold labels.
- Sanitation: Removable drip pans, front-service coils, tool-less baffle removal.
10) MVP Scope (Build Order)
- Static gradient cabinet (no robot) with three sealed sub-compartments and independent loops.
- Pre-cool vestibule drawer with blast fan + coil, temperature logging.
- Manual totes + QR inventory app (phone camera).
- Add single-axis lift serving 6–8 bays → prove cycle time and baffle design.
- Add slotting logic + FIFO, then expand to full AS/RS.
- Integrate weight-based inventory and heat-recovery loop.
11) Risks & Mitigations
- Moisture/frost creep: Use vestibule + dehumidification and tight baffles.
- Complexity vs. reliability: Favor simple shuttle first; modular zones for easy service.
- Noise & vibration: EC fans, resilient mounts, soft motion profiles.
- Cleaning burden: Smooth liners, removable components, CIP-style spray wand for vestibule.
12) Extensions
- Meal-prep mode: Stage tonight’s ingredients to a mid-zone at dinnertime.
- Proofing/fermentation bay: Warm, humidity-controlled mini-zone (isolated).
- Smart grocery: Auto-slot incoming deliveries; generate restock lists.
- Commercial variant: Narrow, deep banks that feed a kitchen pass-through with FIFO totes.
Quick Visual (text-only sketch)